There are only two things that have made any real difference in protecting the public from the dangers of oil trains: activism that has stopped new infrastructure, and low oil prices. While activism is currently on hold during the pandemic, impacts on oil prices abound.
The latest numbers show that U.S. oil-by-rail volumes are down 11 percent versus where they were a year ago, which is likely just the beginning of the decline in volumes.
The industry is actually looking to fill rail tank cars with oil and then just park them as a form of additional storage as the current oil glut, combined with the huge drop in demand due to the coronavirus, is likely to fill all available storage in the next 2-3 months.
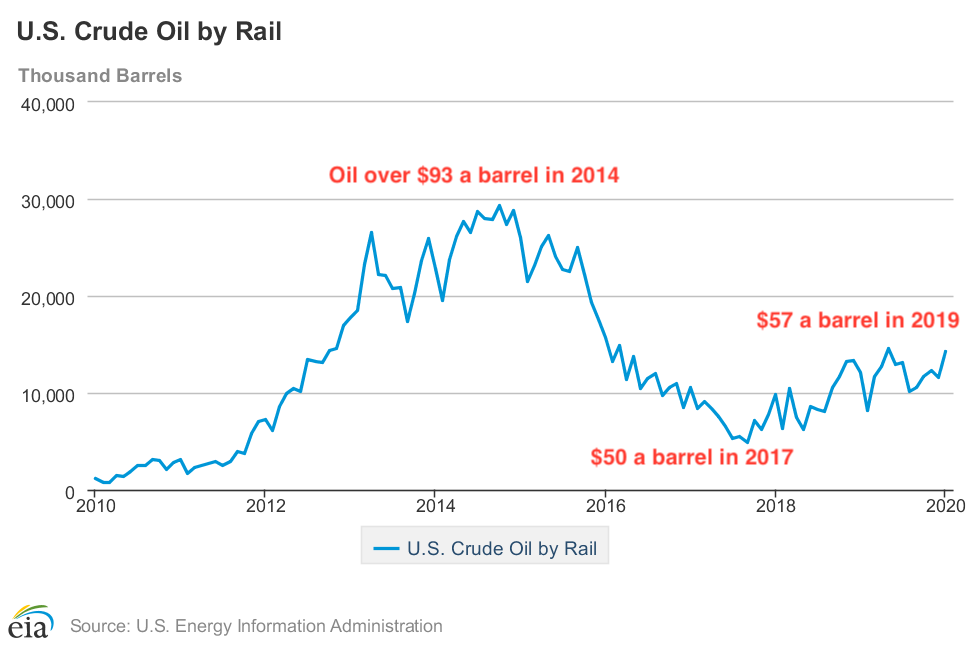
The peak for U.S. oil by rail volumes occurred in 2014 when oil prices were often over $100 a barrel, with an average price just over $93 a barrel for the year.
U.S. oil-by-rail volumes. Credit: U.S. Energy Information Administration
When prices crashed in 2015 and stayed around $50 a barrel for several years, oil-by-rail volumes fell sharply. The main reason for this was that East Coast refineries were able to buy oil more cheaply from African countries than it cost to transport Bakken oil by rail.
The Dakota Access pipeline also began operating in May of 2017 which eliminated the need for as much Bakken oil to be moved by rail.
Bakken oil producers are currently getting well under $20 a barrel for their oil which means moving oil-by-rail is not economically viable due to its higher costs compared to pipelines — especially when even producing the oil is not economically viable. Whiting Petroleum, a large oil producer in the Bakken, just filed for bankruptcy and will likely be the first of many companies to do so.
The cost to lease rail tank cars to move oil has dropped from $1,200 a car to under $700 a car in the past couple of months, an indication of how oil by rail is not a preferred option in this price environment.
Canada’s “Real And Present Danger”
While U.S. oil-by-rail volumes have never returned to the peak levels during high oil prices, Canadian oil-by-rail has been setting records with over 400,000 barrels per day shipped in January. Most of the oil is being sent to the U.S. At the beginning of 2020 I wrote about the coming wave of Canadian oil-by-rail and the risks that it posed.
As Canada moved record amounts of oil by rail, accidents inevitably occurred. The latest happened in February when a train derailed, caught fire, and spilled approximately 400,000 gallons of oil. This followed a similar accident in December, which led an editor at Railway Age to call these Canadian oil trains a “clear and present danger” due to the failure of regulators to address the known risks of moving oil by rail.
However, with Canadian oil prices below $5 a barrel moving oil by rail is no longer viable. Tar sands producer Cenovus Energy transported 120,000 barrels per day of oil in February but has since announced it is shutting down its oil-by-rail operations. The decline in moving Canadian oil by rail will happen fast and the whole industry may follow Cenovus in just shutting down.
John Zahary, CEO of Altex Energy, which had been moving 50,000 barrels per day of oil by rail, told the Global News that the outlook for Canadian oil by rail looked “bleak.”
Landlocked Canadian crude could see prices go negative, meaning producers would pay customers to take oil, Goldman said in note to clients. Shipping it out by rail isn’t economic, and increased production from OPEC nations could displace demand for Canada’s barrels. @ericnuttall pic.twitter.com/ZhYfmtC082
— Alexander Stahel (@BurggrabenH) April 1, 2020
Crisis Is Opportunity for Even More Risk
While the reduction in oil-by-rail volumes will help protect the public from the clear and present danger of oil trains, the industry has successfully lobbied the Federal Railroad Administration for a “60-day emergency waiver for certain requirements of FRA’s rail safety regulations,” which means the oil trains that are on the rails will be even riskier.
Among the safety regulations that have been waived are regulations relating to track inspections, brake operating requirements, and engineer qualifications.
This all is in addition to the regulations that the Trump administration has already removed for oil and ethanol trains, but is consistent with the Department of Transportation’s [DOT] stated position on regulating the rail industry. In May of 2019 that policy was described as follows: “DOT’s approach to achieving safety improvements begins with a focus on removing unnecessary barriers and issuing voluntary guidance, rather than regulations that could stifle innovation.”
BNSF Challenges Court Ruling Over Tribal Rights
In March a federal appeals court upheld a ruling that the Swinomish Indian Tribal Community had the right to stop the major rail company Burlington Northern Sante Fe (BNSF) from transporting trains filled with Bakken oil across their tribal lands.
This is another classic case of railroads acting like they are above the law based on the concept of pre-emption that allows railroads to mosly ignore state and local laws. BNSF has just filed another legal challenge to this latest court ruling, and is once again arguing that it should not have to abide by the court’s decision despite a history of blatantly ignoring the existing agreement with the Swinomish.
The existing agreement between BNSF and the Swinomish allows the rail company to move one train a day in either direction on the tracks in question, but the trains are limited to not more than 25 cars. However, with the beginning of the oil-by-rail boom, BNSF simply ignored that agreement as outlined in the judge’s opinion.
“In 2011, the Tribe learned that BNSF was violating the parallel terms of the right-of-way and the Easement Agreement by running more trains and cars across the Reservation than permitted by its terms. BNSF had also failed for many years to submit to the Tribe the required annual cargo reports. The Tribe requested that BNSF comply with the terms of the Agreement. BNSF refused. The Tribe then sued BNSF in federal district court.”
This type of arrogance is typical from the rail industry, as it always goes back to the argument that local and state laws do not apply to national rail carriers — even to the point of apparently ignoring agreements like the one BNSF had previously signed.
This current legal battle is similar to other upcoming legal arguments about states’ rights to regulate rail safety. Washington State’s regulation limiting the vapor pressure of oil moved by rail will likely be resolved in the courts, as will the efforts by multiple states to require two-person crews on freight trains, which is opposed by the rail industry.
As I have documented over the past six years, and in my book Bomb Trains, one constant tactic of the rail industry is to fight every potential regulation.
Oil-by-Rail: Down But Still Dangerous
While the current economics of the oil industry are likely to greatly reduce the amount of oil moving by rail in North America in the near future, the risks remain. If oil prices return to higher levels at some point in the future, the industry will most likely turn to rail once again. The ability of rail to start up and shut down quickly is what led to the initial oil-by-rail boom in North Dakota, and that flexibility is still appealing to the oil industry.
When the trains do return — as the two recent oil train derailments in Canada clearly illustrate — the very real risks will return with them as the failure of regulators to address the known risks continue to put communities along the rails in jeopardy.
More, wider-view drone footage of today’s derailment from Humboldt, #Sask resident Philippe Gaudet. pic.twitter.com/hSB4FSrQg7
— Guy Quenneville (@gqinsk) February 6, 2020
Main image: Oil tankers. Credit: Carol Von Canon, CC BY–NC–ND 2.0
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay up to date with DeSmog news and alerts