A decision on the proposed northern half of the Keystone XL pipeline – under review since 2008 – hinges on a final environmental review by the State Department now taking into consideration the importance oil-by-rail transport might have on growth of Alberta’s tar sands.
US officials are evaluating the impact Keystone XL will have on expansion of the tar sands and whether or not the pipeline will worsen climate change. According to a new report by Reuters the evaluation has created a balancing test, “zeroing in on the question of whether shipment by rail is a viable alternative to the controversial project.”
The test’s crux: “if there is enough evidence that the oil sands region will quickly grow with or without the 1,200-mile line, that would undercut an argument from environmentalists that the pipeline would turbocharge expansion,” Reuters reports.
President Barack Obama’s State Department is asking rail executives to report on logistics, market dynamics and what obstacles oil-by-rail alternatives face in delivering 830,000 barrels of Canadian oil to Cushing, Oklahoma – the “pipeline crossroads of the world” – where Keystone XL‘s northern half will link up with Keystone XL‘s southern half which is expected to be up and running by the end of October.
In other words, could rail realistically provide an alternative to the Keystone XL, aiding in the expansion of Canada’s highly-polluting tar sands?
With numerous pipeline proposals facing opposition all across Canada and the US, oil-by-rail transport alternatives have picked up some slack. But the high costs associated with rail and the dangers associated with oil-by-rail transport suggest there are real limitations to a full scale tar sands-by-rail revolution.
As Reuters reports, even rail operators admit tanker trains can supplement but not substitute the movement of crude by pipeline.
“We can move large volumes, but it will always be a niche service,” Gary Kubera, owner of Caneuxs, a company expected to move 100,000 [barrels per day] by the end of 2014, told Reuters.
Stew Hanlon, president of Gibson Energy Inc., echoed the sentiment: “We remain very, very confident that rail is here to stay not as a replacement for pipelines, but as a supplement of pipelines.”
Within Canada the oil-by-rail sector has grown tremendously, with five new loading terminals in western Canada and an estimated national transport capacity of 450,000 bpd by next year.
North American Class 1 railways.
Life on the Rails?
Yet the rapid increase in rail transport of crude has led to a series of high-profile accidents in Canada, the most publicized being the Lac-Megantic disaster that saw 47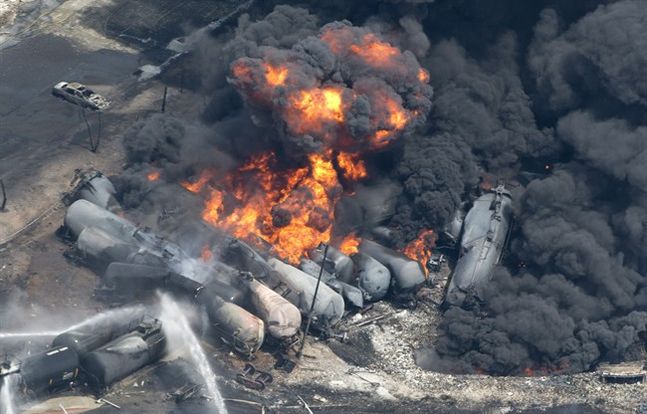 
Just 10 days ago, another tanker train carrying propane and oil derailed outside of Edmonton, Alberta causing an explosion and the evacuation of a small community.
In September a Canada Pacific Railway train carrying oil products derailed in Calgary leading to an evacuation. In July another Canada Pacific Railway train carrying petroleum products slumped over a river after flooding caused a rail bridge to partially collapse.
Yet another Canada Pacific Railway train full of tanker cars carrying oil derailed in Saskatchewan leaking 575 barrels of oil on May 5. The company also had a derailment in Ontario that saw 400 barrels of oil spill, as well as a derailment in March in Minnesota that spilled 24 barrels of oil after 14 cars went off the tracks.
In 2008 trains carried less than 20,000 barrels of oil per day. They now carry roughly 500,000 barrels of oil per day, as of the end of 2012.
According to the State Department, trains have a death rate 3 times higher than pipelines and have a fire and explosion rate 9 times that of pipelines when carrying liquids.
Although groups are quick to point out pipeline disasters happen with less regularity they are often of high-consequence, such as the Enbridge Kalamazoo disaster in 2010 that leaked 20,082 barrels of oil into Michigan waterways. That spill has so far cost more than $1 billion, making it the most expensive onshore oil spill in US history.
Rail Costs Nearly Double Pipelines
According to the Environmental Protection Agency, high costs associated with oil-by-rail transport might pose the largest challenge to operators hoping to gain a larger share of the market. It costs roughly $10 to transport a barrel of oil in a pipeline while the same will cost about $17 via rail.
The industry also has a shortage of terminals capable of refining heavy crude, such as tar sands bitumen from Canada.
The high costs, lagging infrastructure, and dangers associated with rail make the industry an unlikely alternative to the Keystone XL, meaning tar sands transport is unlikely to meet industry expectations should the pipeline be turned down.
For oil producers operating in the tar sands, this inevitably means a shipping glut.
A Risky Investment
Increased oil production in the US has also contributed to dwindling prices for Canadian producers. In June the research firm Wood Mackenzie warned that falling oil prices would lead to break-even points for Canadian energy companies developing one of the costliest forms of oil in the world.
The tar sands are Canada’s fastest growing source of greenhouse gasses and have some investors concerned that the globe’s urgent need to reduce carbon pollution in the atmosphere might diminish the resource’s value.
Just last week a coalition of investors worth $3 trillion pressured 45 of the biggest oil and gas companies to deal with the real concern of “stranded assets,” carbon pools that cannot be developed due to the threat of climate change.
A decision on Keystone XL‘s northern half is due in early 2014. President Obama – who approved the southern half via a March 2012 Executive Order – has indicated he will not approve the northern segment if found to significantly contribute to carbon pollution.
Given the access the pipeline will grant tar sands oil to overseas markets and the advantage pipelines have over rail, the Keystone XL will undoubtedly support tar sands production, promote continued tar sands investment, and contribute to Canada’s already-significant greenhouse gas output.
So, if the decision really comes down to the pipeline’s climate impact – and not something else – the choice is clear.
Image Credit: Wavy1 via Flickr
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay up to date with DeSmog news and alerts