This article by Energy News Network is published here as part of the global journalism collaboration Covering Climate Now.
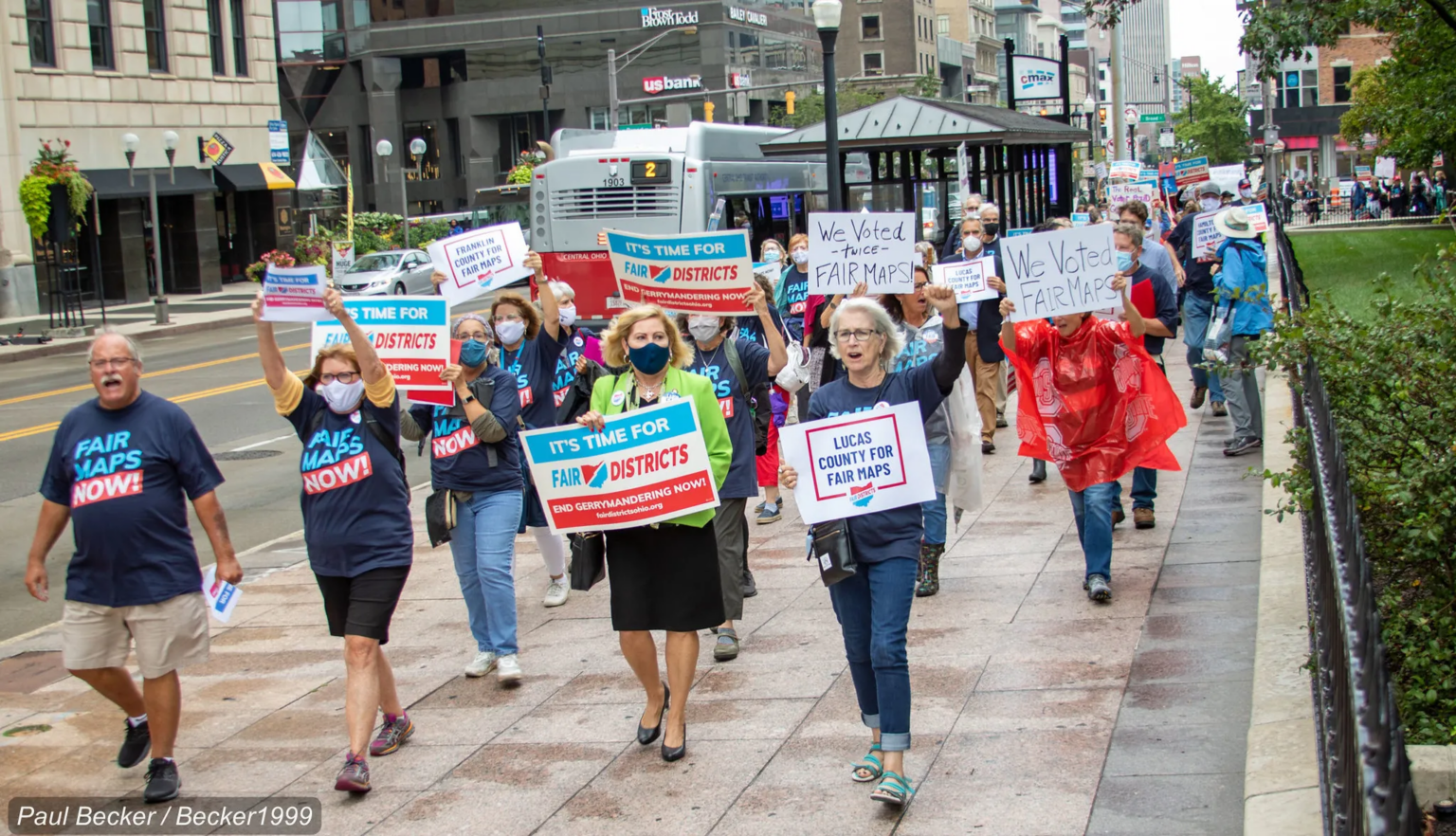
Ohio’s adoption of gerrymandered voting district maps last week is the latest in a series of anti-democratic measures that thwart action to address climate change, critics say.
Data from the Yale Program on Climate Change Communication show a majority of Ohioans believe climate change is happening and worry about it.
A majority also favor regulating carbon dioxide as a pollutant, imposing strict carbon dioxide limits on coal-fired power plants, and research and tax rebates for renewable energy, according to the Yale data. And nearly two-thirds would also require utilities to produce 20% of their electricity from renewable sources.
Over the last decade, however, Ohio lawmakers have subsidized noncompetitive coal plants and erected additional barriers to siting renewable energy.
Ohio also remains embroiled in a corruption scandal relating to House Bill 6. The 2019 law provided bailouts for two former FirstEnergy nuclear plants and two 1950s-era coal plants and revenue guarantees for utilities while gutting Ohio’s previously weakened renewable energy and energy efficiency standards.
Lawmakers repealed subsidies for two former FirstEnergy nuclear plants and a utility recession-proofing provision seven months after the arrests of former House Speaker Larry Householder and others. Yet the rest of HB 6 remains in place, despite multiple repeal bills.
“Ohio is a microcosm of something much bigger,” said Basav Sen, climate justice policy director at the Institute for Policy Studies, referring to a growing trend of anti-democratic moves that hinder progress on climate change. Here are points he and others highlighted to the Energy News Network.
Gerrymandering Rigs Outcomes
“Gerrymandering is manipulating district lines to secure outcomes for some candidates and some political parties,” said Jen Miller, who heads the League of Women Voters of Ohio. The new redistricting maps give Republicans veto-proof majorities of nearly 62% in the House and 70% in the Senate. Fair maps would have roughly a 55% to 45% split between Republicans and Democrats.
Gerrymandering affects all policies, including healthcare, energy, clean water, transit and education, she said. Lawmakers in “safe” districts who owe their election to gerrymandering are more likely to support the party’s agenda, which may not necessarily align with what voters want. And when elected officials don’t have to worry about a tight reelection campaign, they have less incentive to be responsive to constituents.
That lack of engagement makes people less likely to vote, which further suppresses democracy, Miller said. “Gerrymandering, low voter turnout and high voter frustration all go hand in hand.”
“If we’re looking at how to make progress and protect public health and our environment, that shouldn’t be a political issue,” said Miranda Leppla, who heads the environmental law clinic at Case Western Reserve University School of Law.
Yet political parties have become polarized on the topic. So, “we still have parts of HB 6 on the books that have been shown by a court of law to not only have been moved forward illegally — but that remain in place because of the party in power — which are harming human health,” Leppla said.
Similarly, when Senate Bill 52 passed in 2021, it erected additional barriers to siting solar and wind projects, but not fossil fuel energy. All yes votes came from Republicans, with only a few siding with Democrats, who all voted no.
Gerrymandering Also Enables Corruption
Corruption itself erodes government legitimacy and undermines democracy, according to Transparency International. And gerrymandering can set the stage for it.
“Gerrymandering is the manipulation of elections, leading to less accountability,” said Catherine Turcer, executive director of Common Cause Ohio. “As a consequence, gerrymandering fuels corruption because elected officials don’t worry about their constituents. They focus on their donors, their political party and themselves.”
Indeed, to prevent corruption, “you need strong tools and instruments of accountability,” said Neil Waggoner, federal deputy director for energy campaigns at the Sierra Club. Without it, “you see the corruption … that was the case with HB 6 and Larry Householder.”
And, Waggoner added, “a lot of folks that were around are still in power.” Many lawmakers who voted for HB 6 were in “safe” districts, and none who were up for election in November 2020 lost their races.
“If we truly had competitive districts in Ohio, I don’t think you would have seen HB 6,” said Rep. Sean Brennan, D-Parma, who has taught American government at the high school level. He sees the 2019 law at the center of Ohio’s ongoing corruption scandal as the “quintessential example” of an anti-democratic result of gerrymandering.
Dark Money and Other Corporate Spending Sway Policy
“What we see are literally corporations using their financial clout to steer public policy in their direction and for their benefit at the expense of the general public,” Sen said. “Dark money is behind a lot of it.”
Dark money refers to spending to influence public policy, where the funds can’t be traced to the original donors. Former U.S. Attorney David DeVillers has said dark money nonprofit groups are ripe for abuse as a money laundering tool.
Evidence at Householder’s trial showed FirstEnergy, its affiliates and others spent roughly $60 million on HB 6. Prior to Householder’s arrest, public records revealed only a tiny portion of that money.
More recently, the Energy and Policy Institute linked The Empowerment Alliance, which has multiple gas industry links, to a political action committee that spent more than $1 million on last year’s elections. The group has also promoted state and local legislation labeling natural gas as “green energy.”
Additionally, the Center for Media and Democracy has found links between dozens of Ohio lawmakers and ALEC, the American Legislative Exchange Council, a corporate-funded group that favors fossil fuel development and opposes renewable energy standards. At least seven lawmakers on a committee set up under a 2014 law that cut back and froze Ohio’s clean energy standards for two years were members of ALEC.
Corporations also spend lots of money in plain sight at both the state and federal levels, Sen said. As a group, for example, utilities, fossil fuel industries and nuclear interests have long ranked among Ohio’s top givers for reported political donations.
Voter Suppression Hurts People Most Impacted by Pollution
“Voter suppression is in front of us right now and it’s becoming greater as the days go by,” said Ericka Copeland, director of the Sierra Club of Ohio. HB 458, signed by Gov. Mike DeWine in January, adopted strict voter ID requirements. The law also shortened the time frame for early voting, limited the use of ballot drop boxes, curtailed curbside voting, and imposed limits on provisional ballots.
“The very people who are most adversely affected by the corporate interests that dominate our government today are the very people whose votes are silenced,” Sen said. Under-resourced communities — disproportionately people of color — face higher risks from pollution and energy costs.
Without financial resources to sway policies and elections, “all they’ve got is their vote,” said Ashley Brown, who formerly served on the Public Utilities Commission of Ohio.
Other Limits on Public Engagement
When SB 33 criminalized various activities under the guise of protecting “critical infrastructure,” the 2021 law limited people’s ability to organize and protest against pipelines and other fossil fuel industry activities, Sen said.
More recently, HB 507 labeled natural gas “green energy” and jumpstarted proposals to drill under state parks and wildlife areas. A pending lawsuit challenges the law for violating the state constitution’s single-subject rule and for lawmakers’ failure to hold any public hearings on it after the natural gas provisions were added.
“These are absolutely anti-democratic, because they’re not allowing people to participate in what our state government is passing,” said Leppla, who is one of the attorneys representing the Ohio Environmental Council in the case.
The single-subject rule matters, Leppla said, because “a really important component of democracy is that people can understand what’s moving through our statehouse.” HB 507 started as a simple two-page poultry bill but swelled to 88 pages as more subjects were lumped in. Likewise, the failure to hold hearings after the addition of the oil and gas provisions prevented people from testifying against those provisions before the bill became law, she noted.
“The comment period is an essential part of Ohioans having access to elected officials’ ears, to be very clear about what they worry about and the consequences,” said Turcer at Common Cause Ohio. This summer’s scandal about fabricated comments on drilling proposals compounds the problem, she said, because it becomes harder for public officials to trust the comments they do get.
People’s voices are also silenced by state laws limiting local governments’ authority to take action on a wide range of issues, including environmental matters, budgets and gun violence, Turcer said. For example, a 2021 law prohibits local governments from banning natural gas or propane hookups in new buildings.
“The next step in corporate control would be to ensure that the electorate is not informed,” Sen said. “And one way to do it is by interfering with public education.”
Pending legislation would gut diversity, equity and inclusion programs and require “both sides” teaching about climate change policy and other “controversial” topics at state colleges and universities. SB 83 is “definitely raising concerns about equity and opportunity and inclusion,” Copeland said, noting that the Sierra Club of Ohio opposes the bill.
What Can Be Done?
“One of the things that’s clear is all of the different ways that hurdles are put before Ohioans who are just trying to make sure that we can breathe clean air and drink clean water,” Turcer said. “But what is clear to me is that people want to take power to improve their communities. They want to use the tools that are available to them to get more accountable government, and to ensure that citizens have their rights. And that is a huge upside.”
In August, voters rejected a Republican-backed amendment that would have made it nearly impossible to pass citizen-initiated constitutional amendments. A reproductive rights amendment is on the ballot this fall, and efforts are underway to get an amendment on next year’s ballot to put a nonpartisan commission in charge of redistricting. Future amendments might address a wide range of issues, including potentially climate change, Turcer said.
The history of social movements also offers hope for getting more action on climate change, Sen said. He cited the 20th century’s pushes for labor unions and civil rights as examples. Each movement “came from the bottom up. It came from popular pressure that got so strong that at some point in time, the people in power had to concede.”
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay up to date with DeSmog news and alerts