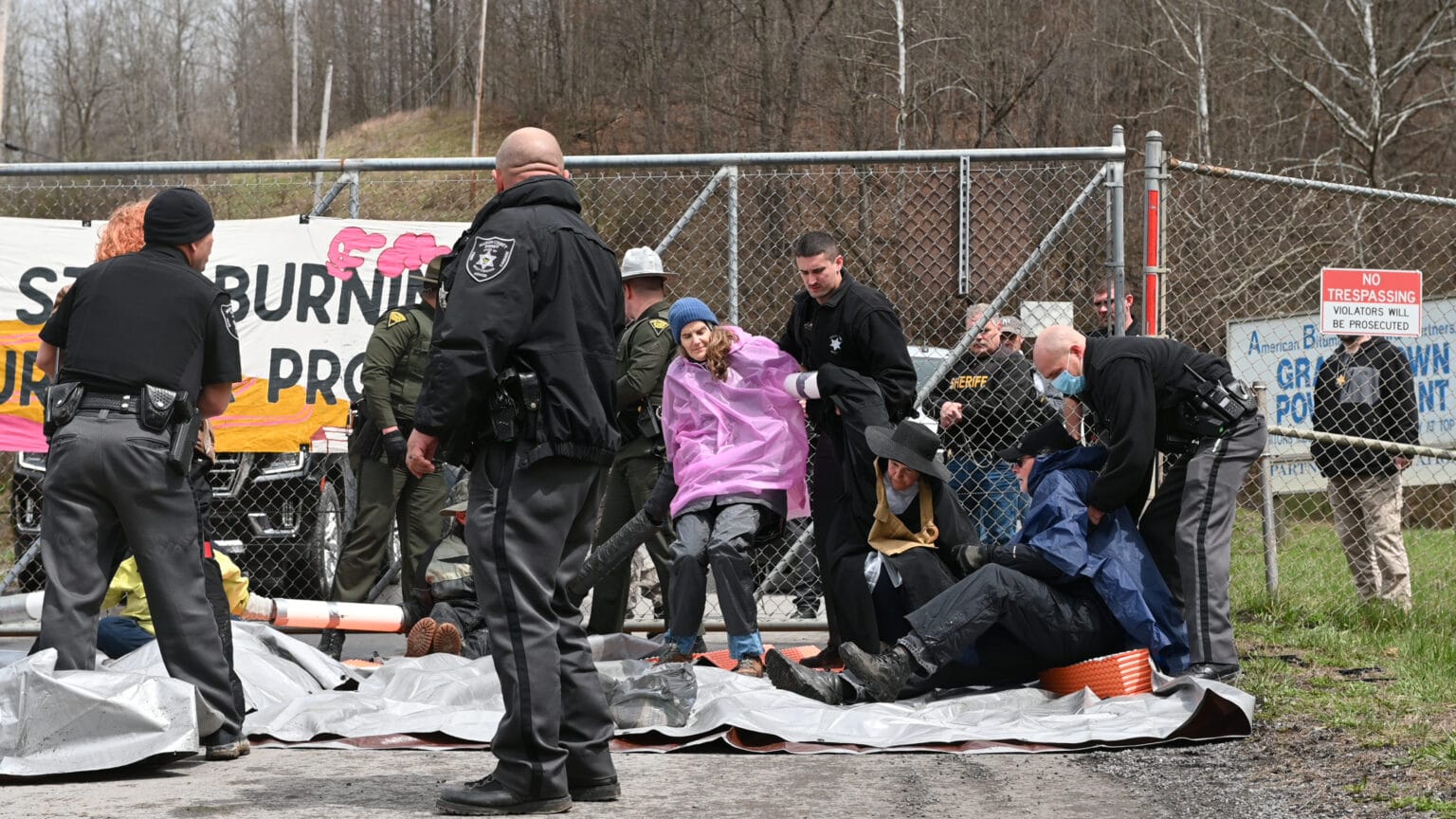
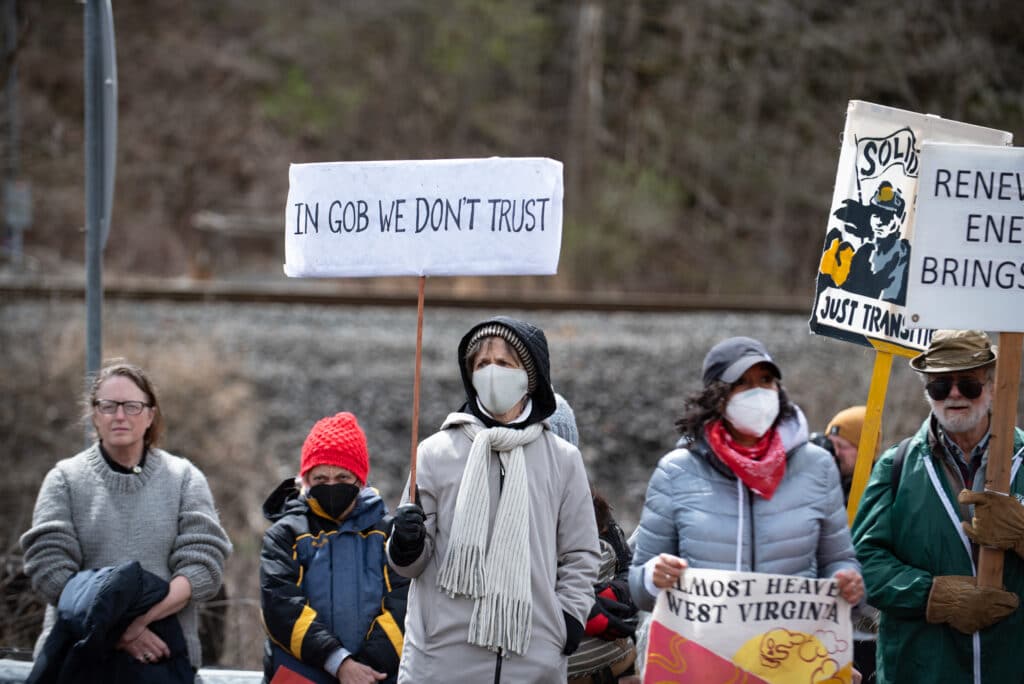
On Saturday, April 9, a group of more than 50 activists from the region and around the country convened on a coal power plant in West Virginia, calling for it to be closed and rallying around a small blockade outside its entrance. By the end of the day, 16 of them had been arrested.
The plant the protesters targeted, in Grant Town, West Virginia, isn’t just any of the over 200 coal power plants still operating in the United States. It’s the one where Sen. Joe Manchin makes nearly $500,000 per year selling a dirty coal waste called “gob.”
Gob is short for “garbage of bituminous,” which, according to VICE News, Sen. Manchin sells to the power plant for a tidy profit via Enersystems, the company he founded and that his son now runs.
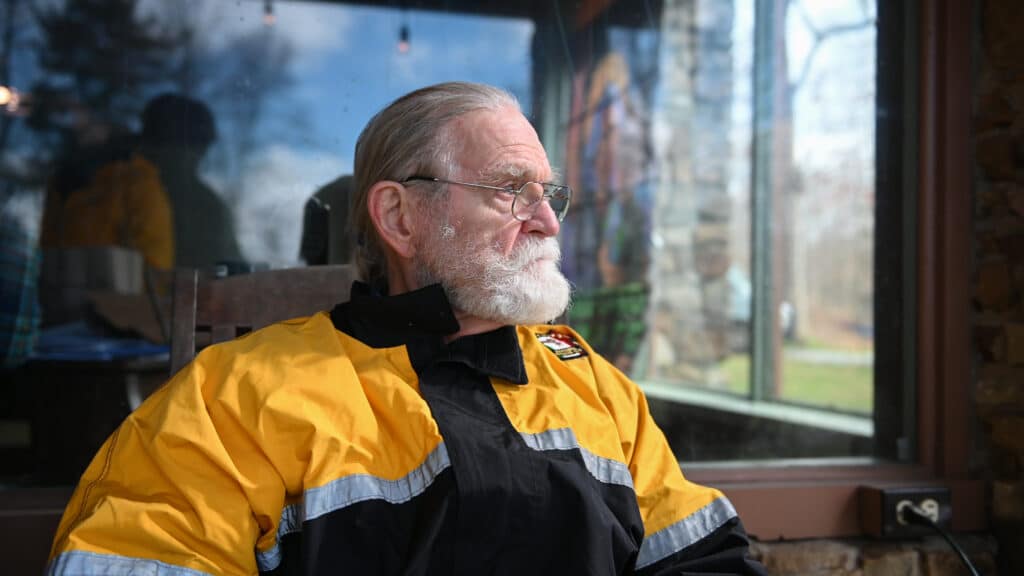

The protesters, a mix of local and national activists, call themselves West Virginia Rising. One of them was Michael Whitten, a retired miner from Boone County, West Virginia. “When I worked on strip mines, we threw that [gob] away,” Whitten told DeSmog. “We covered it up, it’s like if you had a wood-burning stove at your home and you wanted to put wet wood in it — it’s just not economical.”

He’s right. The West Virginia customers served by the Grant Town Power Plant, run by American Bituminous Power Partners (AMBit), are being charged more because of the gob. In the last six years burning this waste coal has cost the local power utility an additional $117 million, according to documents analyzed by The New York Times. All of this — even though regulators initially fought the plant’s transition to burning gob — was pushed through thanks to Sen. Manchin.

Manchin, who has a blind trust set up for his investments, has continually been a one-man blockade for climate legislation. That came to a head this year when he essentially killed the Build Back Better bill, Biden’s signature climate and social policy legislation, by dropping his (some might argue never serious) support of it. He closed his statement with, “I will continue working with my colleagues on both sides of the aisle to address the needs of all Americans and do so in a way that does not risk our nation’s independence, security and way of life.”
Around 2:00 p.m. on Saturday, activists trickled in from a nearby campground where they had received some training and information about legal support. For those who chose to put themselves in position to be arrested by the West Virginia state troopers already on the scene, it was going to be a long day.
Marion County Sheriff Jimmy Riffle stated that those arrested would not likely be released until the late evening. The sheriff, who spoke from behind the coal plant’s fence, explained where the property lines were — and anyone who crossed them would be arrested.
Sleeping Dragons Arrive

It all happened quickly. Several members of the group laid down tarps on the pavement, while others hung a banner that read “Manchin: Stop Burning WV’s Future for Profit” on the coal plant’s front gate. Then the “sleeping dragons” came in.
Arms linked together through lengths of PVC pipe, half a dozen protesters formed a human chain in front of the gate. But the blockade only lasted a short time. State troopers picked up the interlocked protesters and moved them closer to their squad cars, where they could figure out how to disconnect the activists. That cleared the plant’s driveway but many more activists were still rallying in front of the gate — in the legal middle ground between the property and the road.
Eventually, the troopers had separated all but two of the arrestees. That pair was put in a police car while still attached.
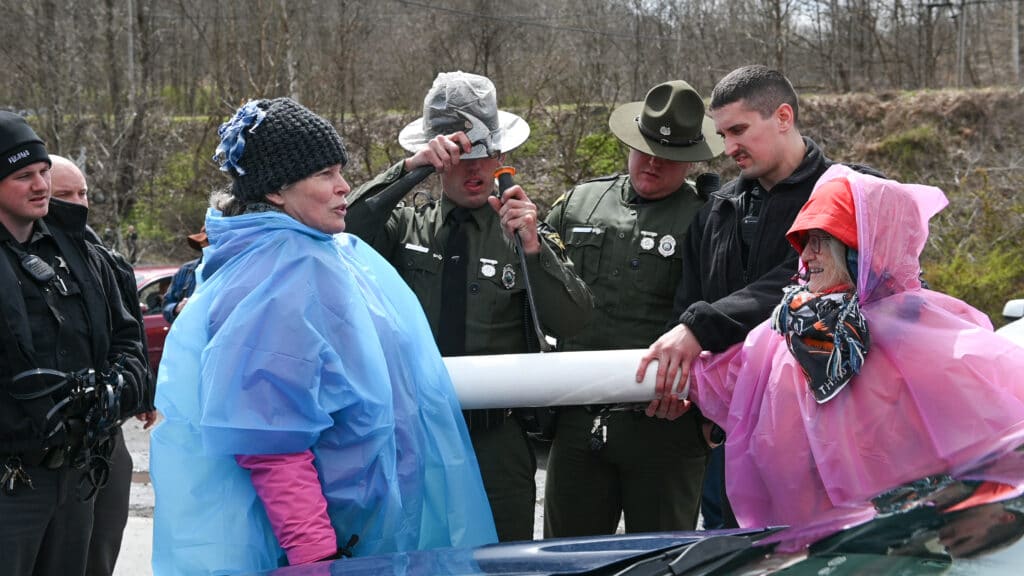


Among those eventually arrested was Joanna Smith, who seemed unperturbed by the three troopers around her, one chiseling away at the piping connecting her to another arrested activist, Donna Shaunese. Smith told me over the sound of alarming cracks and crunches that the chiseling didn’t bother her.
She thought that the issue of climate change was important enough to be arrested over, and that doing something that might get the attention of Sen. Manchin was vital. “At this point, everybody knows what needs to be done.”

Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay up to date with DeSmog news and alerts