In over their heads with debt, U.S. shale oil and gas firms are now moving from a boom in fracking to a boom in bankruptcies. This trend of failing finances has the potential for the U.S. public, both at the state and federal levels, to be left on the hook for paying to properly shut down and clean up even more drilling sites.
Expect these companies to try reducing their debt through the process of bankruptcy and, like the coal industry, attempting to get out of environmental and employee-related financial obligations.
The Bankruptcy of EP Energy
In October, EP Energy — one of the largest oil producers in the Eagle Ford Shale region in Texas — filed for bankruptcy because the firm couldn’t pay back almost $5 billion in debt, making it the largest oil and gas bankruptcy since 2016.
EP Energy hasn’t produced a profit since 2014 and Bloomberg reported that the company would need oil to be at “a price closer to $70 per barrel” for EP to be profitable. Oil has not come close to averaging over $70 a barrel since 2014.
Despite its financial struggles at current low oil prices, the company plans to continue operating after restructuring and eliminating up to $3 billion in debt. However, EP has not identified any funds that it would be setting aside for well cleanup, which is not unusual for an oil and gas company.
In response, as part of the bankruptcy proceedings, the U.S. Department of the Interior filed a document arguing that EP Energy is still responsible for its obligations to assure the “decommissioning, plugging, and abandonment” of any of the EP Energy wells that are located on leased federal and tribal lands.
Ideally, that would mean EP Energy sets aside funds for the proper cleanup and end-of-life processes for its oil and gas wells, which number more than 800 in the Eagle Ford region.
However, the federal government hasn’t even named a number yet for how much that should be. The Bureau of Land Management and Bureau of Indian Affairs “are currently still assessing the status of reclamation and plugging and abandonment obligations across the Debtors’ onshore federal and Indian leases,” writes the Interior Department.
In EP Energy #bankruptcy, US Interior Department wants to make sure that enough money is set aside for cleanup. For financially struggling companies, cleanup is becoming the tail that’s wagging the dog. https://t.co/LDrnMr01rn
— Clark Williams-Derry (@ClarkWDerry) November 16, 2019
The federal government is only getting around to assessing EP Energy’s potential liabilities once the firm is already in the bankruptcy process, revealing one of the flaws in the current system. Federal and state governments have not been holding fracking companies fully liable for the environmental damage and cleanup costs of their drilling activity.
Joshua Caleb Macey, a visiting assistant professor at Cornell law school who specializes in bankruptcy and energy law, told DeSmog that the situation with EP Energy was “frustrating and completely normal.”
According to the Interior Department filing, “Regardless of its bankruptcy, the Debtor is required to comply with all applicable federal laws.”
As I’ve reported before, oil and gas companies are legally required to hold a certain amount of funds to pay for well cleanup costs, a process known as bonding that varies by state and for public lands.
Because companies are rarely required to have those funds available before they start drilling (and thanks to industry-friendly regulators and politicians), in reality oil and gas companies can walk away from cleanup obligations with relative ease, which has become the pattern for bankrupt coal companies.
Including Cleanup Costs Would Make Extraction ‘Uneconomic’
Federal and state regulators have been failing to require companies to fully fund expected cleanup liabilities, which helps mask the true cost of oil and gas production. Passing environmental cleanup costs on to the taxpayer amounts to a backdoor subsidy for the oil and gas industry.
Requiring oil and gas companies to pay for shutting down and cleaning up wells would greatly increase the cost of drilling for many oil and gas wells. The fracking industry already can’t make money pumping fossil fuels out of shale in the U.S., and that’s without these firms coming even close to fully funding their cleanup costs.
However, more state governments are realizing the scale of this problem and starting to look at increasing and enforcing bonding requirements for oil and gas well cleanup. However, in oil-rich places like Alberta, Canada, and Alaska, regulators are realizing that the money just isn’t there.
Hey @jkenney @Alberta_UCP after your sustained attacks on the Liberal government, why are you now begging for taxpayer money to clean up Alberta’s abandoned oil wells? Oil companies must pay for that. Not us. Hands off our tax dollars. The oil shareholders should pay. #cdnpoli
— Trish Palmer (@TrishPalmerYVR) December 1, 2019
In 2018, the natural gas driller Amaroq Resources acquired the Nicolai Creek assets in southwest Alaska from the bankrupt Aurora Gas. This transaction was delayed when the Alaska Oil and Gas Conservation Commission (AOGCC) announced $7 million in bonding required for the gas wells associated with the purchase. This is the point where the state government had the power to make Amaroq provide adequate bonding for well cleanup.
The AOGCC then agreed to reduce that amount to $200,000 and the deal went ahead.
Since that deal, the commission increased the minimum statewide bonding level to $400,000 per well for the first one to 10 wells. Amaroq would be required to abide by these new regulations and has appealed this decision. Company president Scott Pfoff explained that these new bonding requirements make the business “uneconomic.”
And that is the reality. If oil and gas companies were required to pay for the full end-of-life cost of their wells, much of their inventory becomes uneconomic. This is where taxpayers come in.
Fracking Industry Wants to Dump Wastewater in Streams and Rivers to Save Money
Failure to require adequate bonding for oil and gas cleanup costs is just one of many backdoor government subsidies for the oil and gas industry. The failure to regulate flaring and venting of the potent greenhouse gas methane during oil drilling is another example.
Fracking firms, which spend a lot of borrowed money to pump out a lot of oil and gas for not much (or any) profit, are experiencing a collapse in financing. Thanks to the industry’s failed business model, these companies are desperate for ways to cut costs.
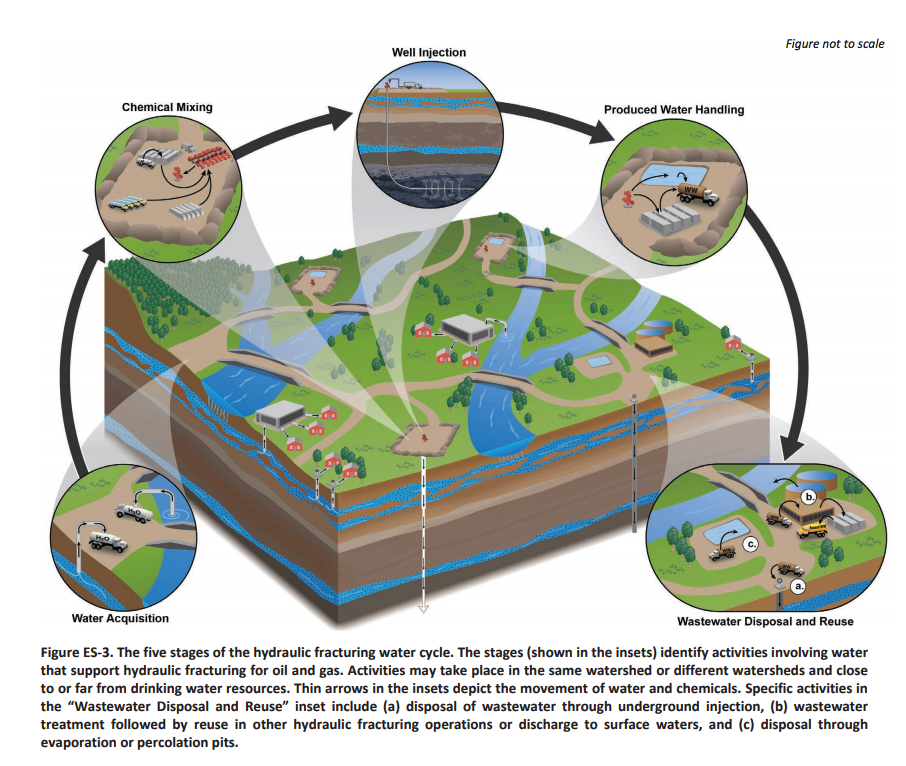
One of the major costs associated with hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, is acquiring, pumping, and disposing of water, which, after a driller is finished with it, typically contains corrosive levels of salts and contaminants including naturally occurring radioactive materials, chemicals, and oil residues. This area has become a major target for the industry to save money.
A graphic showing the water cycle during hydraulic fracturing. Credit: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, 2016
As the Washington Post pointed out in 2015 (and as I highlighted last year), when it comes to fracked shale oil and gas production, “currently there is no way to treat, store, and release the billions of gallons of wastewater at the surface.” The industry’s current range of (legal) approaches to disposing of its massive amounts of wastewater involves injecting it underground, which in some cases is tied to increased earthquake activity, using it to irrigate crops or de-ice roads, and sending it to municipal water treatment plants lacking equipment to properly treat it.
Treating oil and gas drilling wastewater is possible, but expensive. As S&P Global Platts recently reported, according to a study by the Texas Alliance of Energy Producers and Independent Petroleum Association of America, for Permian drillers in Texas, “Economically, treatment costs must come down.”
The study concludes that dealing with wastewater is already a limiting factor in this prolific region: “Some Permian sub-basins are currently constrained due to insufficient injection well capacity. Projected production growth will worsen the situation.”
With this glut of wastewater combined with high costs, the industry is looking for a cheap alternative. The latest preferred approach seems to be lobbying governments to change the rules to allow dumping wastewater with limited treatment into rivers and streams.
In November, E&E News reported that there’s movement to allow or expand such wastewater dumping in Oklahoma, Texas, New Mexico, and Pennsylvania, all states with major fracking industries. “Within a year, Oklahoma could get approval from EPA to start issuing permits that will allow the oil industry to dispose of briny oil field waste in waterways,” E&E wrote.
As space for injection wells becomes scarce, the industry hopes to dump its wastewater in streams and rivers, once again passing on potential environmental and financial liabilities to the public.
A 2017 working group looking for alternatives for Oklahoma oil field wastewater (also known as “produced water”) found “the most cost-effective means of reducing disposal is for oil companies to treat and clean that produced water so it can be reused for things like fracking,” reported NPR‘s StateImpact Oklahoma.
However, recycling produced water to again frack wells results in more toxic produced water, which can’t be recycled indefinitely. With injection wells increasingly unable to handle the volume of water produced by the industry, shale firms have been seeking cheap alternative disposal methods, including dumping the water in rivers and streams.
However, the 2017 analysis concluded that treating produced frack water to the point it could be safely dumped into rivers or used to irrigate agriculture wasn’t economically viable.
Owen Mills, the director of water planning for the Oklahoma Water Resources Board, explained to StateImpact Oklahoma why this wasn’t an option for the industry: “It’s incredibly expensive to do that and it takes a lot of energy.”
To properly treat the fracking wastewater to the point it is no longer a threat to human health and the environment would be incredibly expensive, and that is why the industry is lobbying to change the rules about disposing its wastewater. If it succeeds, expect the eventual clean up costs — also incredibly expensive — to be billed to the American public.
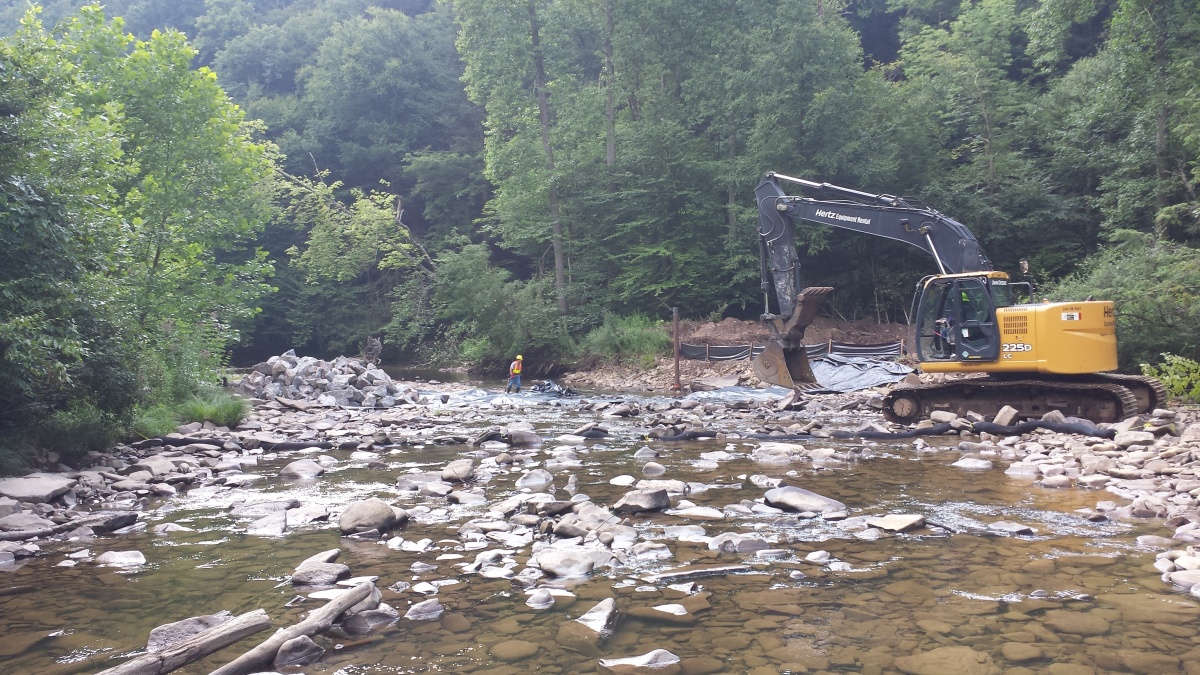
Main image: Heavy equipment sits on the edge of a rocky stream bank as part of U.S. Bureau of Land Management-Forest Service reclamation efforts for abandoned oil and gas wells in the eastern U.S. Credit: Bureau of Land Management
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay up to date with DeSmog news and alerts