What should be done about a chemical plant in Louisiana’s St. John the Baptist Parish that releases chloroprene — a chemical so toxic that the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) determined nearby residents face the highest risk in the country of developing cancer from air pollution?
The answer is simple, according to Retired Lt. Gen. Russel Honoré: “Fix it, move it, or shut it down.” Honoré is founder of the Green Army, a coalition of environmental groups and concerned citizens fighting against pollution in their communities.
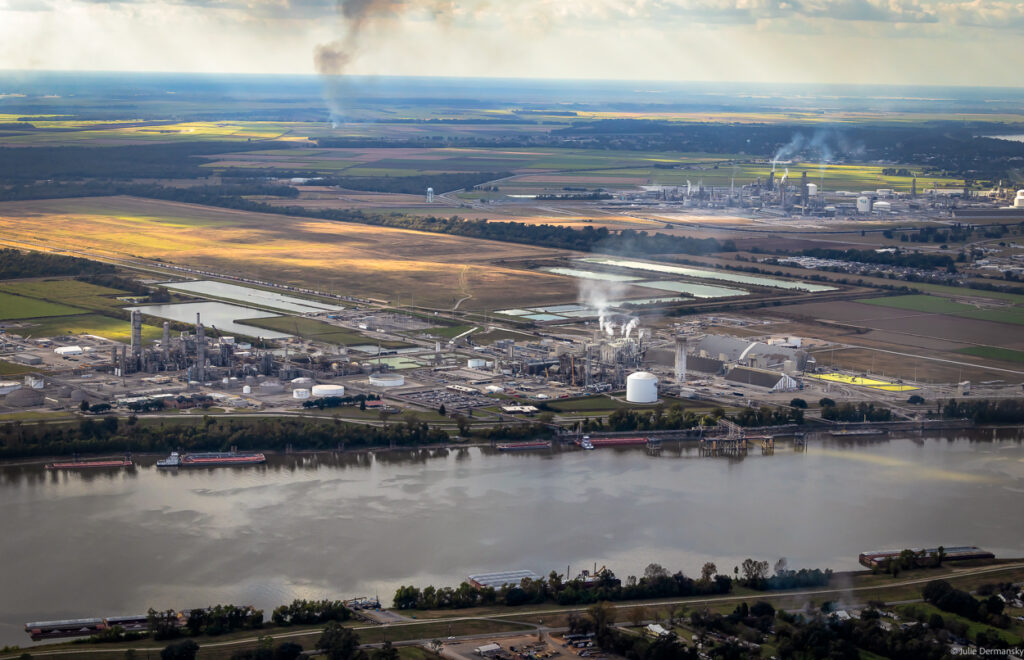
But local, state, and federal regulators haven’t resolved issues swirling around emissions released by the Denka Performance Elastomer plant, located in LaPlace, Louisiana. The plant is next to the Mississippi River, on a stretch of land between New Orleans and Baton Rouge known as Cancer Alley.
Chloroprene Emissions on the Decline But Still Too High?
DuPont’s synthetic rubber plant in LaPlace emitted chloroprene for 46 years before it was sold to Denka. Shortly after Denka took over the plant, the EPA reclassified chloroprene in 2010 as a likely human carcinogen. The EPA deems 0.2 micrograms per cubic meter the acceptable standard for chloroprene emissions, a level that the plant overshoots considerably.
EPA’s 2010 Toxicological Review of Chloroprene determined that short-term exposure to high levels of chloroprene can cause a range of health impacts, from dizziness to chest pains, and suggests that chloroprene causes an increased risk of lung, liver, and kidney cancers, as well as leukemia and immune-system problems.
Though Denka doesn’t agree with the EPA’s findings, the company agreed in January 2017 to reduce chloroprene emissions by 85 percent. It installed costly emissions reduction equipment that began operating at full capacity in March 2018. Emissions are trending downwards, but not to the level that EPA scientists say is the threshold for dangerous exposure or to a level that state or federal regulators are satisfied with.
In June 2017, Denka challenged the agency’s findings on chloroprene’s toxicity, prompting the EPA to formally review its 2010 assessment. After completing the review at the end of January 2018, the EPA backed its findings, but Denka has filed an appeal, which is still under review.
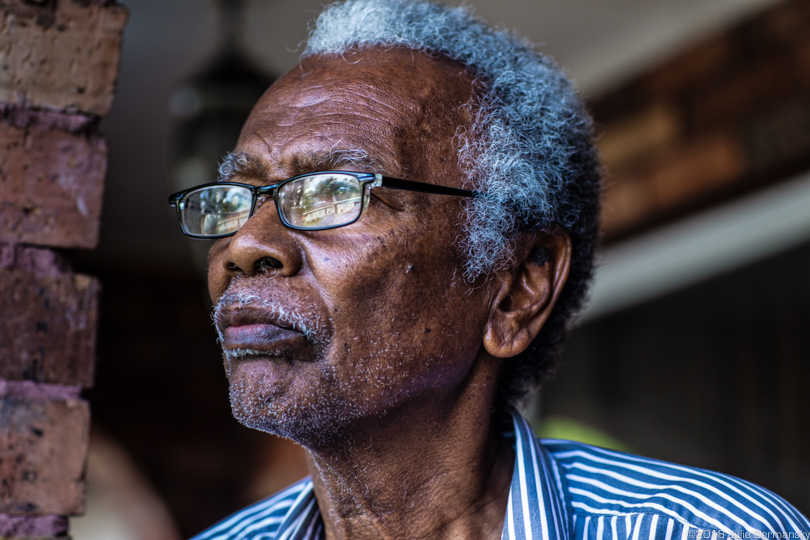
Robert Taylor outside of his home about a mile from the Denka chemical plant.
Robert Taylor, founder of Concerned Citizens of St. John the Baptist Parish, a community group borne out of the fear of breathing toxic air, welcomed the EPA’s findings. “We all knew there was something wrong with our air, and then the EPA put a name on it,” he says.
It makes sense that Denka would challenge the EPA’s findings, but the Concerned Citizens group is frustrated with Louisiana’s Department of Environmental Quality (LDEQ) and Department of Health, which also question them.
At a parish council meeting in December 2016, Chuck Carr Brown, head of the LDEQ, accused members of the group of fear-mongering for insisting Denka cut chloroprene emissions to the EPA’s recommended standard.
Brown stands firm that the EPA’s figure of 0.2 micrograms is for guidance; it is not a legal standard that the plant is required to meet. The current standard was set years before the EPA reclassified chloroprene as a likely human carcinogen.
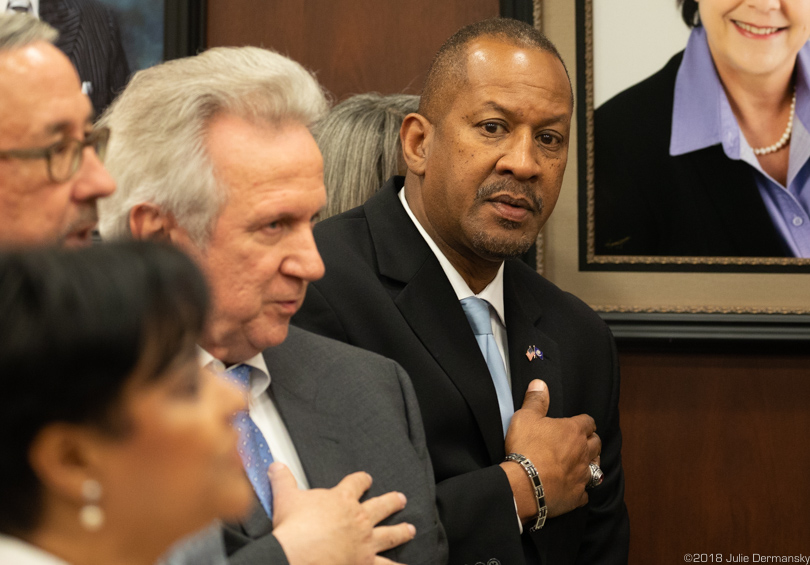
Secretary of the LDEQ Chuck Carr Brown (right) next to Jimmy Guidry, M.D., Louisiana’s top health officer.
At an April 24, 2018 meeting of the St. John the Baptist Parish Council, Brown said that the EPA’s number might not be the final standard, once Brown and others have a chance to study results of Denka’s emissions-reduction efforts.
“Currently there is not an ambient air quality standard for chloroprene,” Jennah Durant, an EPA representative said in an email. “EPA, state, and company on- going actions are designed to reduce chloroprene emissions from the plant.
At the same meeting, Jimmy Guidry, M.D., the top state health officer and medical director, declared that people living near the plant do not face a health emergency and downplayed chloroprene’s health risks.
Councilman Lennix Madere, Jr, questioning state officials at the April 24 parish council meeting.
But when pressed by Councilman Lennix Madere, Jr., who represents the district closest to the plant about what Guidry would feel comfortable saying is a safe level, Guidry did not contradict the EPA’s 0.2 microgram suggested standard. “The EPA has come out and set their number that they calculated from a mathematical formula and until we can prove otherwise we should strive to get to that number,” Guidry said.
Brown gave the council assurances that the emissions levels were much lower than before, and that his agency is continuing to work with Denka to reduce emissions as much as possible.
But Wilma Subra, a technical advisor with the Louisiana Environmental Action Network (LEAN) who has been advising the Concerned Citizens group, told the council that Denka has shown an unwillingness to lower production (which immediately would reduce emissions) or to spend additional money on emissions reduction measures beyond its previous commitment.
Members of the Concerned Citizens of St John the Baptist Parish at a parish council meeting.
Members of the citizens group who attended the parish council meeting were disappointed that the council seemed to accept Brown and Guidry’s wait-and-see attitude. After the meeting, Taylor reached out to Honoré, who since then has been strategizing with the citizens group on what he sees as an undeniable environmental justice issue.
Assessing the Health Risks to Students
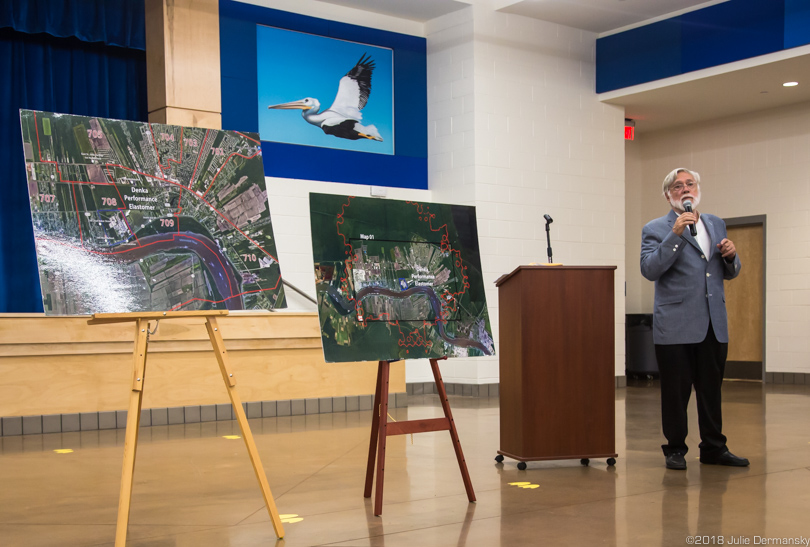
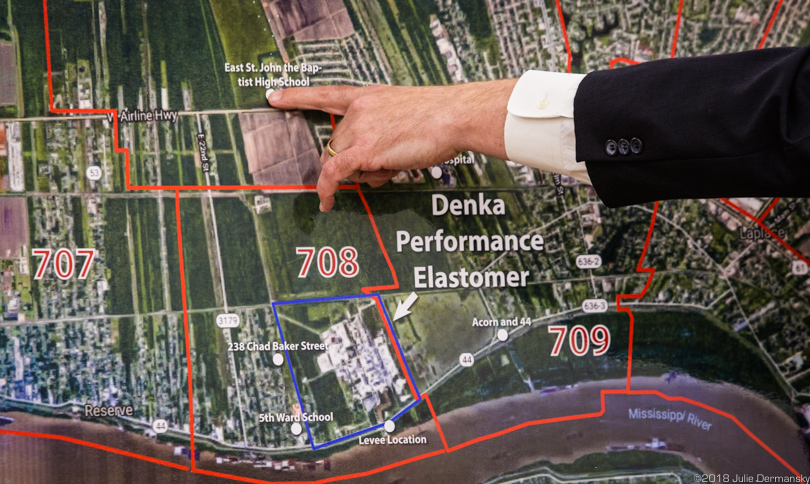
Detail of a map around the Denka plant that shows the areas in St. John the Baptist Parish with the highest levels of chloroprene exposure, including two schools.
In March this year, the St. John the Baptist School Board expressed concern about the safety of children attending the school closest to the Denka plant, leading to a parish council request to the state to review potential health risks.
As a result, the Louisiana Department of Health examined whether potential health risks would be significantly reduced if the children were sent to another school nearby.
On July 6, the department released an assessment indicating that moving students at the Fifth Ward Elementary School, about a half-mile west of the Denka plant, to East St. John Elementary, which is three miles north of the plant, “would not greatly decrease their theoretical risks of developing excess cancers from exposure to chloroprene.”
The preliminary assessment was based on data limited to air sampling results from March to May 2018 and collected after Denka activated its emissions reduction devices.
Subra questions the assessment’s value. She said that looking at a few months of data to determine the risk to students misses the long-term effects of higher exposure that children and their families experienced before the equipment was installed.
The Department of Health’s findings don’t surprise Denka, because the company believes chloroprene is being cast unnecessarily as a dangerous chemical. “There is no evidence to suggest our operations pose any increased risk of health impacts to our surrounding community,” Jim Harris, a spokesperson for Denka, said in an email.
John Cummings is one of the lawyers involved in a lawsuit against Denka and DuPont by residents of St. John the Baptist Parish. The suit is seeking injunctive relief and monetary damages for various issues, including health-related problems and lost property value.
He, too, questions the premise of the state’s health assessment and the timing of its release.
“What sense does it make to consider the value of moving children from one area with bad air to another?” asks Cummings.
The lawsuit, filed in July 2017, is still pending. Federal Judge Martin Feldman denied granting class action status to the lawsuit in March due to a missed deadline. The same judge is expected to rule very soon on a motion by Denka’s attorneys to dismiss the suit altogether.
Disputing the State Health Assessment
Taylor called the state’s health assessment irresponsible. “It is unbelievable that people in positions of authority would make the statement that the Department of Health has made since we became aware of the EPA’s findings,” Taylor said. He gives the report no credence because he can’t see the value in a health assessment that doesn’t include input from the people who live in the community.
The concerned citizens group is anxiously awaiting a health assessment from a Stanford Human Rights Clinic team, which spent weeks earlier this year conducting a randomized health survey of households within a 1.5 mile radius of the Denka plant. The group helped the Stanford team survey more than 500 area households, gathering data on incidences of cancer, other medical diagnoses, and health symptoms.
Members of the Concerned Citizens group and a team from Stanford Human Rights Clinic at a gathering after the team’s on-the-ground health survey work was completed on March 29, 2018.
As far as Taylor knows, no one from the Department of Health has ever asked anyone impacted by the chloroprene emissions about their health. The department confirmed it has not spoken with people in the community near the plant about their health issues since the EPA reclassified chloroprene as a likely human carcinogen.
Instead, the department relies on the Louisiana State University Tumor Registry, which collects data on cancer diagnoses. But the tumor registry relies on reported cases of cancer in Louisiana only, and some cases go unreported while others are treated and diagnosed out of state.
State officials and Denka representatives point to the registry’s findings as an explanation for why they think the EPA assessment of cancer risk for St. John the Baptist Parish is wrong. A recent assessment broken down by zip codes doesn’t show an elevated risk of two types of cancer that have chloroprene as a risk factor, according to Robert Johannessen of the Department of Health’s communication office.
Attorney John Cummings at a school board town hall meeting in LaPlace, Louisiana.
“The tumor registry is malarkey,” Cummings told me. “If you go down some streets and talk to people, you will find 80 percent of the households have a family member with cancer.”
“There is clearly something fishy going on here,” Taylor said. “Otherwise, why won’t these state officials sit down and face us?”
He thinks the citizens group’s demands are quite reasonable. “We aren’t asking officials to shut the plant down. We just don’t want them to be allowed to go on poisoning us.”
I asked Councilman Madere if the council planned to take any further actions. He told me what happens next is up to the EPA. He said that without a legal standard for emissions, there is nothing anyone at the state level can really do.
I asked the EPA if or when it plans to set a standard for chloroprene emissions, but did not receive an answer.
“While they are looking at numbers on a report, I’m taking care of my daughter and my wife,” Taylor said. Last year, after his wife had a stroke, he convinced her to move to California. He was afraid the air-borne chemicals from the plant, about a mile from their home, would interfere with her recovery.
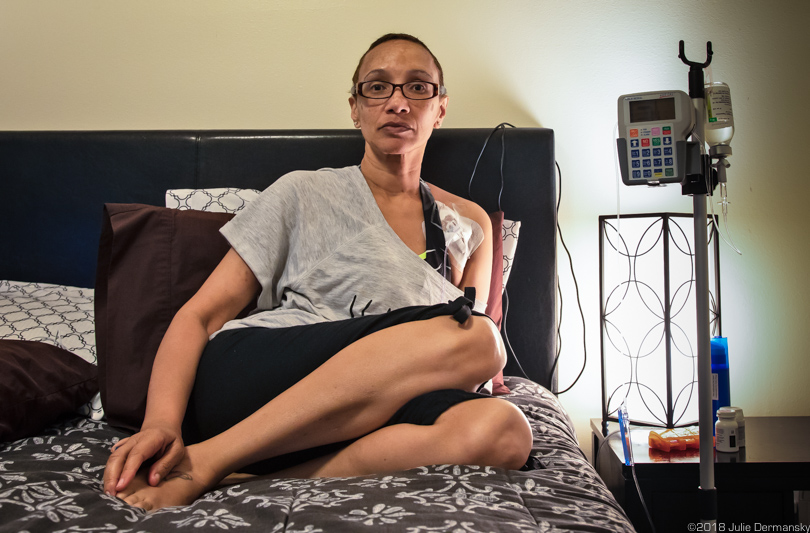
Robert Taylor’s daughter, Raven Taylor, homebound due to a rare autoimmune disease.
Taylor would also like to relocate his daughter, Raven, who suffers from an immune deficiency condition — which EPA’s assessment says is in line with high chloroprene exposure — but the family’s financial situation has prevented the move. He now splits his time between Louisiana and California.
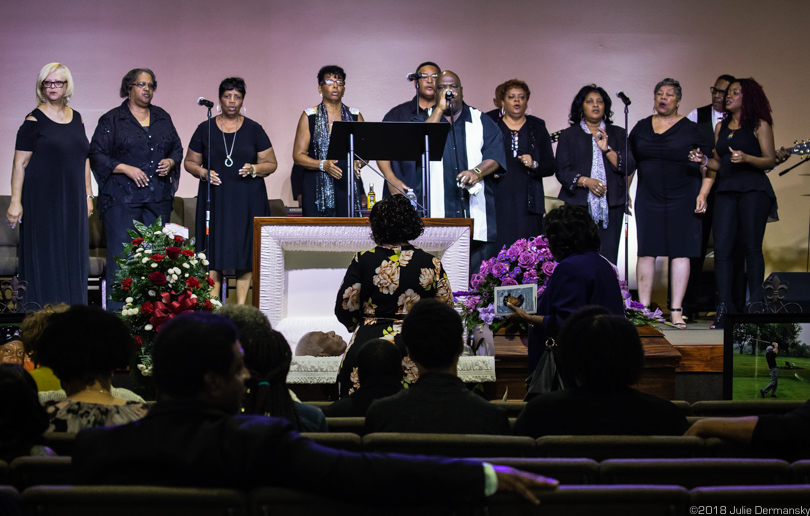
He regrets being unable to attend the funeral of Walter Gerard, a member since the beginning of the Concerned Citizens of St. John the Baptist Parish. Gerard died of cancer on June 27. “How many more members will we lose before we get clean air?” Taylor wonders.
Funeral for Walter Gerard.
Main image: Denka plant in Laplace, Louisiana, on March 29, 2018. Credit: All photos by Julie Dermansky for DeSmog
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay up to date with DeSmog news and alerts