The Trump administration officially announced Monday that it will scrap fuel economy and emissions targets for cars and light-duty trucks sold in the United States and set new weaker standards, effectively undermining one of the federal government’s most effective policies for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
As the New York Times and the Los Angeles Times anticipated late last week, the two agencies responsible for auto standards — the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) — both claimed that their internal reviews have found the Obama-era standards to be too strict, and that the agencies would go back to the drawing board to revise standards for model years 2022-2025.
The weaker standards, expected to be revealed in coming months and reported to be well below the current targets of 54.5 miles per gallon (or roughly 35 miles per gallon in real-world driving conditions), will be celebrated as a victory for the automakers, which have been lobbying the Trump administration since the day after the presidential election and which used a major trade group to peddle climate science denial in support of the rollback.
“The Obama administration’s determination was wrong,” EPA administrator Scott Pruitt said in a statement. “Obama’s EPA cut the Midterm Evaluation process short with politically charged expediency, made assumptions about the standards that didn’t comport with reality, and set the standards too high.”
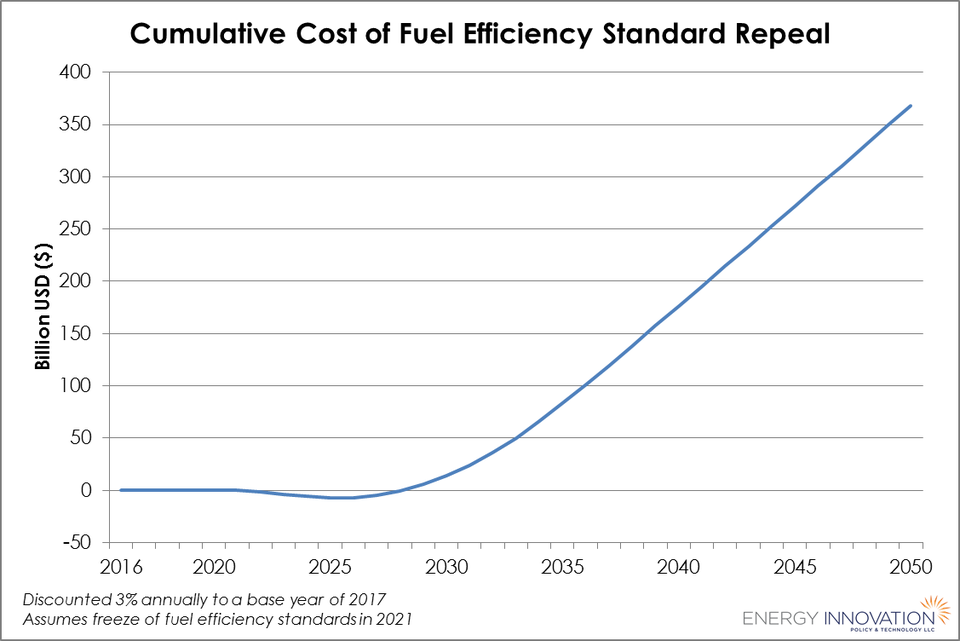
Many argue, however, that weakened standards will hurt the average driver, who will have to pay more for gasoline to fuel the less efficient vehicles. Energy Innovation’s peer-reviewed modeling simulator, for instance, shows how a rollback on emissions standards would cause nearly $400 billion in increased consumer costs between now and 2050.
Freezing fuel efficiency standards at 2021 levels would cost approximately $370 billion by 2050. Credit: Robbie Orvis/Energy Innovation
Furthermore, weakening mileage and emissions standards will set up a fight with California, which has a unique authority under the Clean Air Act to set its own emissions standards for vehicles, and state authorities are signaling that they have no intention of chasing the federal government in a race to the bottom. Notably, over recent weeks, Pruitt has been publicly critical of California’s authority to set its own standards, leading many to speculate that the EPA might attempt to revoke California’s waiver under the Clean Air Act.
“California is not the arbiter of these issues,” Pruitt told Bloomberg TV. The state, he said, “shouldn’t and can’t dictate to the rest of the country what these levels are going to be.”
On Monday, a so-called conservative coalition sent a letter to Pruitt and Secretary of Transportation Elaine Chao applauding the decision, which had yet to be formally announced. Organized by Tom Pyle of the Koch-funded Institute for Energy Research, and signed by Michael Needham of Heritage Action, Brent Gardner of Americans for Prosperity, Myron Ebell of the Competitive Enterprise Institute, and Grover Norquist of Americans for Tax Reform, the letter goes so far as to say that “we believe repealing the entire program is appropriate and warranted.”
The Auto Alliance Used Climate Denial to Push its Agenda
Most automakers selling cars in the United States have been actively lobbying President Trump and the respective agencies to rewrite and weaken the rules. This is despite the fact that, in the wake of the financial crisis and $80 billion bailout of Detroit, the car companies helped design these regulations and publicly accepted the mileage and pollution standards.
Through the powerful Alliance for Automobile Manufacturers (or Auto Alliance) trade group, which counts Toyota, Ford, General Motors, Fiat Chrysler, BMW, Mercedes, and Volkswagen among its members, the automakers sent a letter to President Trump days after the presidential election, and then another near-identical one to Pruitt after he was confirmed to lead EPA.
In the year since, pressure from the group has increased, and the Alliance has resorted to a disinformation campaign founded in climate science denial and cherry-picked data.
In February, as NHTSA was reviewing the Obama standards, the Alliance sent a report to the agency that presented a number of studies and resources intended to undermine the current standards and present the case for rolling back the targets. The report was written by an industry-connected team from Air Improvement Resources, Inc, along with Joseph D’Aleo, a policy adviser to the Heartland Institute, a fountainhead of climate denial.
Despite its name, Air Improvement Resources is a for-profit consultancy with a long history of combating environmental regulations. Their client tally includes a long list of organizations found in Desmog’s Climate Disinformation Database, including the American Petroleum Institute, the American Coal Council, the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, and the American Enterprise Institute.
The report itself relies heavily on comments from the automakers and on papers that were paid for by the industry or fossil fuel interests. Perhaps the most striking example is the citation of a study by Anthony Cox, Jr. that questions the health impacts of fine particulate air pollution (such as smog), a study that was directly funded by the American Petroleum Institute.
The Alliance’s report also promotes outright climate science denial, with an entire section dedicated to questioning climate models. Other sections cherry-pick lines from studies to undermine the scientific consensus linking the burning of fossil fuels with more extreme droughts and floods, hurricanes, ocean acidification, and wildfires.
The Auto Alliance Wants You to Think It’s Serious About Selling Cleaner Cars
Meanwhile, last week at the New York International Auto Show, the Auto Alliance, along with the Association of Global Automakers and more than a dozen automakers announced a new marketing campaign to “to increase electric car use throughout the Northeast.”
According to the campaign’s website: “Drive Change. Drive Electric. represents a unique public-private partnership between auto manufacturers and Northeast states to advance consumer awareness, understanding, consideration, and adoption of electric cars, including battery electric, plug-in hybrid electric, and fuel cell electric vehicles. By showcasing to drivers and passengers the convenience, affordability, technology, sustainability, and power performance of electric vehicles, Drive Change. Drive Electric. aims to put more electric cars on the road than ever before.”
However, the effort is coming at precisely the same time that the Auto Alliance and its members has been actively lobbying for looser emissions standards, which would lower car companies’ incentives for selling more electric vehicles.
As Fred Lambert writes on the popular electric car enthusiast site Electrek:
“They are launching this just as the EPA is about to release its decision over the fuel consumption standard that those same organizations have been pressuring them to lower.
If it does get lower, they wouldn’t have to mass produce electric vehicles for a few more years and continue to focus on smaller numbers of EVs [electric vehicles] in CARB [California Air Resources Board] states, like in the Northeast.”
California May Save the Auto Industry From Itself
The announcement opens the door for a new weakening of efficiency and pollution standards, but automakers will have to wait months before they know what targets they will have to achieve by 2022. Further complicating matters is California’s unique authority under the Clean Air Act to set its own air pollution standards. Publicly, California officials have offered firm resolve in sticking with the existing, stricter standards.
“We are not going to go backward,” California Attorney General Xavier Becerra told the Los Angeles Times. “We are not interested in a race to the bottom … We are prepared to take whatever action, legal or otherwise, we have to to protect our health and our economy.”
Twelve other states and the District of Columbia have adopted California’s standards, meaning that roughly 40 percent of the light-duty vehicles sold nationally will still have to comply with current standards.
Automakers do not want to have to produce two different types of vehicles within the American market, and have repeatedly argued on behalf of one national standard.
California officials will have plenty of support from the other states, as well as from many business groups and even automobile parts manufacturers. In March, a group of 46 businesses — including major employers like Kellogg, Levi Strauss, Nike, and Unilever — sent a letter to Pruitt warning against a rollback of emissions standards.
Meanwhile, vehicle parts manufacturers boast that the Obama standards have created jobs in the auto industry. In March, the Motor & Equipment Manufacturers Association, the Manufacturers of Emission Controls Association, and the Aluminum Association all announced they are joining forces as the Automotive Technology Leadership Group, with a goal of advocating for continuing current fuel economy standards and reducing emissions.
“Do not slow down the pace on CAFE [Corporate Average Fuel Economy] standards,” said James Verrier, president and CEO of Borg Warner, a major auto equipment manufacturer. “We’ve come a long way as an industry and we need to keep going forward. Don’t go backwards and don’t slow down.”
Meanwhile, in Europe and China — the world’s other two largest auto markets — carmakers are complying with ever-stricter standards, and any rollback of U.S. regulations would make American companies laggards globally. Chinese officials have even signaled a plan to end all sales of gasoline and diesel-powered vehicles. “I don’t really know if the auto industry wants what this administration might be doing,” Harvard law professor Jody Freeman told the New York Times. “It might be like the dog that caught the car.”
A lesson could be learned from the last time that the auto industry resisted fuel efficiency improvements. For nearly two decades, the fuel efficiency standards, known as CAFE, held mostly static around 25 miles per gallon. By 2008, when the financial crisis struck, American demand for cars dropped considerably, and demand for gas-guzzling SUVs plummeted even faster. Combined with high gas prices, the 20-plus year run of flat fuel efficiency ended in a massive bailout of Detroit’s Big Three automakers as American car companies lost market share to more fuel-efficient German and Japanese cars.
The Auto Alliance’s own marketing claims that many electric cars are already cheaper to own than gas-guzzling alternatives. Meanwhile, a whopping 87 percent of American drivers want better fuel economy out of their cars, and 73 percent think the government should raise standards to get it.
Instead, the Trump administration has announced its intention to weaken standards, relying on misinformation provided by the Auto Alliance and its members, which will make it more expensive for Americans to drive and makes the entire auto industry less competitive globally.
Main image: Rolling back fuel efficiency standards in the U.S. could cost drivers an additional $370 billion by 2050. Credit: Oak Ridge National Labs, public domain
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay up to date with DeSmog news and alerts