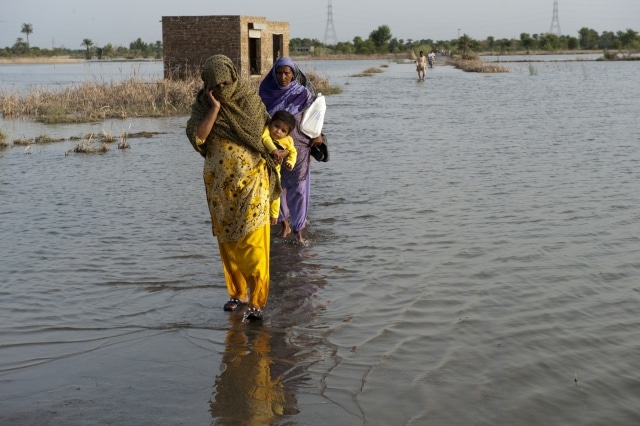
An astonishing 720 million people around the world face falling back into extreme poverty unless we tackle climate change immediately, warns a new report by the Overseas Development Institute (ODI).
The report was published as world leaders gathered this week at the United Nations General Assembly and agreed the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), among which is the eradication of extreme poverty by 2030.
This goal is achievable, according to the ODI, but not without a greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions peak in 2030, and a fall to near zero by 2100. “Climate change increases the probability that those who emerge from extreme poverty will be at risk of falling back into it,” it concludes.
Beyond 2030
Sustaining poverty reduction therefore relies on curbing climate change the report argues.“If the global community is serious about eradicating extreme poverty for good, it needs to think beyond 2030. Eradicating poverty by 2030 will be no great accomplishment if we are incapable of sustaining that achievement from 2030 onwards.”
It continues: “It is policy incoherent for big GHG emitting countries, especially industrialised ones, to support poverty eradication as a development priority, whether through domestic policy or international assistance, while failing to shift their own economy toward a zero net emissions pathway.”
As the report notes, progress on poverty eradication over the past two decades has reduced the percentage of people living on less than $1.25 a day in the developing world – defined as the extreme poor – from 43 percent in 1990 to about 17 percent as of 2011.
“In order to stop poverty, we must stop climate change.” – Jay Winter Nightwolf, Echota Cherokee nation. #ActOnClimate
— Sierra Club (@sierraclub) September 24, 2015
Analysing data on the impact of climate change on food prices, the effects of childhood malnutrition and stunting, the productivity of primary sectors (such as agriculture or mining), and increased droughts, the ODI estimates that up to 720 million people are at risk of facing extreme poverty from 2030 to 2050 under a business-as-usual scenario. As the report starkly points out, this is roughly the same number of people that exited extreme poverty over the last two decades.
However, this number is likely to be much higher if the effects of sea-level rise, an increase in airborne diseases, and conflict – among other climate impacts – are factored into calculations.
Ecomodernist Manifesto
The ODI report comes at the same time as a group of individuals calling themselves the ‘Ecomodernists’ launched their manifesto in London yesterday – among those promoting it include self-styled ‘climate lukewarmist’ Matt Ridley, and former environment secretary and climate denier Owen Paterson.
As the manifesto explains, ecomodernism believes in human rights and freedoms – chief among these, the alleviation of global poverty.
However, in contrast to the ODI’s report, their manifesto goes on to argue that “climate change and other global ecological challenges are not the most important immediate concerns for the majority of the world’s people. Nor should they be.”
Instead, technology should be the main driver in helping developing countries to achieve modern living standards and end material poverty it says. This includes intensive agriculture, nuclear energy, reforestation and urbanisation. Furthermore it argues that renewable energy is inadequate for meeting global energy demands and that there need not be a limit to economic growth.
Economic Growth
But as the ODI argues: “While [economic] growth is unquestionably part of reaching zero extreme poverty, relying on high growth rates alone to achieve this goal would be unwise. First, recent high growth rates may not be sustained. Projecting them decades into the future paints an overly optimistic view of extreme poverty in 2030.
“In reality, economic growth has become increasingly less effective at reducing poverty because of the increasing inequality of that growth. Since 2005, inequalities have widened even further in developing countries, leading to lower rates of poverty reduction than would have been the case if inequality had remained constant.”
Achieving a zero-emissions future, with peak emissions within 15 years, requires all countries to “transform” their economies, the ODI explains. Deep domestic GHG cuts are part of developed countries’ obligation it says, with middle and low-income countries also ensuring their current investment choices reduce their forecast emissions.
“This presents a global challenge that some argue conflicts with the goal of eradicating extreme poverty,” ODI acknowledges, “However, early evidence suggests low-emission economic development, although radically different from historic experience, is consistent with the combination of moderate, sustained and pro-poor growth and reductions in inequality needed to eradicate poverty.”
Therefore addressing growth and inequality together is “far more likely to reduce poverty than a strategy reliant on attempts to maximise growth alone, based on unrealistic projections.”
Agriculture and Cities
Pointing out that industrialised agriculture is a significant contributor to GHG emissions, the ODI looks to the World Bank which argues that “improving the productivity, profitability and sustainability of smallholder farming is the main pathway out of poverty in using agriculture in development.”
Doing so presents a “major synergy”, says the ODI, for reducing poverty and emissions “where there is the institutional capacity and political will to limit the land-use conversion of forests and other natural stores of GHGs.”
And on urbanisation, the ODI agrees it can drive positive change but only if city planners and policymakers tackle poverty and climate change together rather than “entrench and perpetuate old problems for new people”.
“The impact of unchecked climate change creates an insurmountable challenge for the zero poverty target,” it argues, “but climate change mitigation need not.”
Photo: Asian Development Bank via Flickr
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay up to date with DeSmog news and alerts